7. The Gridsim Input/Output¶
The input/output module provides loader and saver interfaces.
Currently Gridsim provides loader for CSV file (CSVReader) and savers
for CSV file (CSVSaver) and images – .png, .jpg, .pdf, etc. –
(FigureSaver).
7.1. Input¶
-
class
gridsim.iodata.input.Reader(self)¶ Bases:
objectThis class is the based class of all readers/loaders.
-
clear(self)¶ Empties the data of the Reader.
-
load(self, data_type=None, nb_data=float("inf"))¶ This method MUST returns formatted data following this format
[(label1, data1], (label2, data2), ...]with:
labelX: a strdataX: a list ofdata_type
Parameters: - data_type (type (default None)) – the type of stored data if
Noneno conversion are done. - nb_data (int) – the number of data to load
Returns: a dict of values
Return type: dict
-
-
class
gridsim.iodata.input.CSVReader(self)¶ Bases:
gridsim.iodata.input.ReaderThis class reads a CSV file and stores the data as follow:
[(label1, data1], (label2, data2), ...]with:
labelX: a strdataX: a list ofdata_type
Parameters: stream (str or every type managed by withkeyword) – a stream of data or a file name-
DEFAULT_DATA_NAME= 'DATA_'¶ If no header, the label of the
dictreturned bygridsim.iodata.input.CSVReader.load()will beDATA_XwithXan integer representing the column in the file:0 <= X < column number - 1
-
clear(self)¶ Removes all data stored in the object.
Returns:
-
class
gridsim.iodata.input.CSVTimeReader(self)¶ Bases:
gridsim.iodata.input.CSVReaderThis class reads a CSV file and stores the data as follow:
[(label1, data1], (label2, data2), ...]with:
labelX: a strdataX: a list ofdata_type
Parameters: stream (str or every type managed by withkeyword) – a stream of data or a file name-
load(self, data_type=None, nb_data=float("inf"))¶ Loads the data from the given CSV data file.
Parameters: - data_type (type) – the type of the stored data if
Noneno conversion are done. - nb_data (int
.. warning:: The first column is consider as time column.
nb_dataMUST have the sameunitas the time in the stream) – the time the load MUST stop
- data_type (type) – the type of the stored data if
7.2. Output¶
Module author: Gillian Basso <gillian.basso@hevs.ch>
Code author: Michael Clausen <clm@hevs.ch>
Code author: Gillian Basso <gillian.basso@hevs.ch>
This module provides interfaces to save data.
To use the Saver a class has to implement the AttributesGetter
interface.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | from gridsim.unit import units
from gridsim.simulation import Simulator
from gridsim.thermal.core import ThermalCoupling, ThermalProcess
from gridsim.thermal.element import ConstantTemperatureProcess
from gridsim.recorder import PlotRecorder
from gridsim.iodata.output import FigureSaver, CSVSaver
# Gridsim simulator.
sim = Simulator()
# Create a simple thermal process: Two rooms and the thermal coupling between
# them and to the outside temperature.
# __________ ___________
# | | ________________ | |
# | room1 |]-| room1 to room2 |-[| cold_room |
# | 18 C | |_____50_W/K_____| | 25 C | outside 5 C
# 10 W/K -[| | | |]- 10 W/K
# |__________| |___________|
#
celsius = units(18, units.degC)
room1 = sim.thermal.add(ThermalProcess.room('room1',
50*units.meter*units.meter,
2.5*units.metre,
units.convert(celsius, units.kelvin)))
celsius = units(25, units.degC)
room2 = sim.thermal.add(ThermalProcess.room('room2',
50*units.meter*units.meter,
2.5*units.metre,
units.convert(celsius, units.kelvin)))
celsius = units(5, units.degC)
outside = sim.thermal.add(
ConstantTemperatureProcess('outside', units.convert(celsius, units.kelvin)))
sim.thermal.add(ThermalCoupling('room1 to outside',
10*units.thermal_conductivity,
room1, outside))
sim.thermal.add(ThermalCoupling('room2 to outside',
10*units.thermal_conductivity,
room2, outside))
sim.thermal.add(ThermalCoupling('room1 to room2',
50*units.thermal_conductivity,
room1, room2))
# Create a plot recorder that records the temperatures of all thermal processes.
kelvin = PlotRecorder('temperature', units.second, units.kelvin)
sim.record(kelvin, sim.thermal.find(has_attribute='temperature'))
# Create a plot recorder that records the temperatures of all thermal
# processes in Kelvin.
celsius = PlotRecorder('temperature', units.minutes, units.degC)
sim.record(celsius, sim.thermal.find(has_attribute='temperature'))
# Create a second plot recorder which records all energy flows
# (thermal couplings) between the different processes.
flow = PlotRecorder('power', units.second, units.watt)
sim.record(flow, sim.thermal.find(element_class=ThermalCoupling))
print("Running simulation...")
# Run the simulation for an hour with a resolution of 1 second.
sim.run(2*units.hour, 1*units.second)
print("Saving data...")
# Save the figures as images.
FigureSaver(kelvin, "Temperature (K)").save('./output/fig1.png')
FigureSaver(celsius, "Temperature (C)").save('./output/fig2.png')
FigureSaver(flow, "Flow").save('./output/fig3.png')
CSVSaver(celsius).save('./output/fig2.csv')
|
- On lines 46, 51 and 57, we create
Recorderobjects. - On lines 47, 52 and 58, we add the recorders to the simulation.
- On lines 68 to 70, we use the recorders as
AttributeGetterto save them in figure. Here, the 3 images file saved:
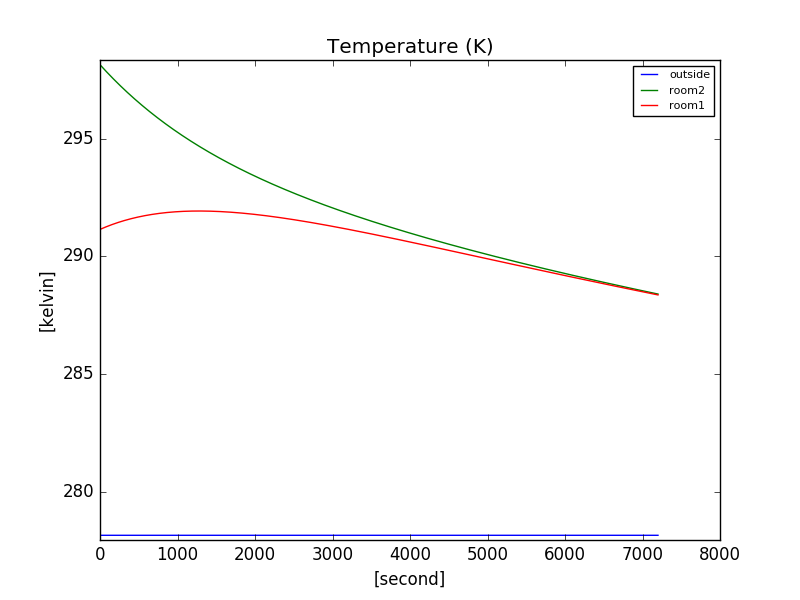
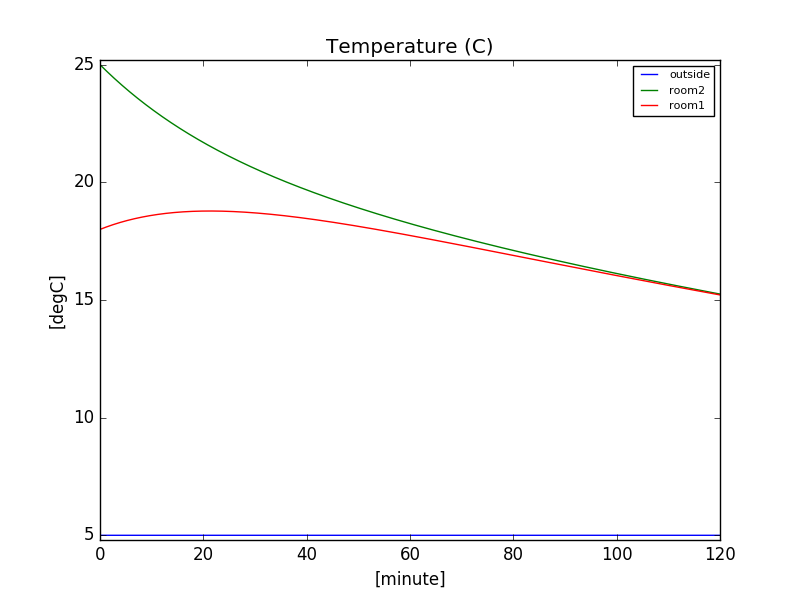
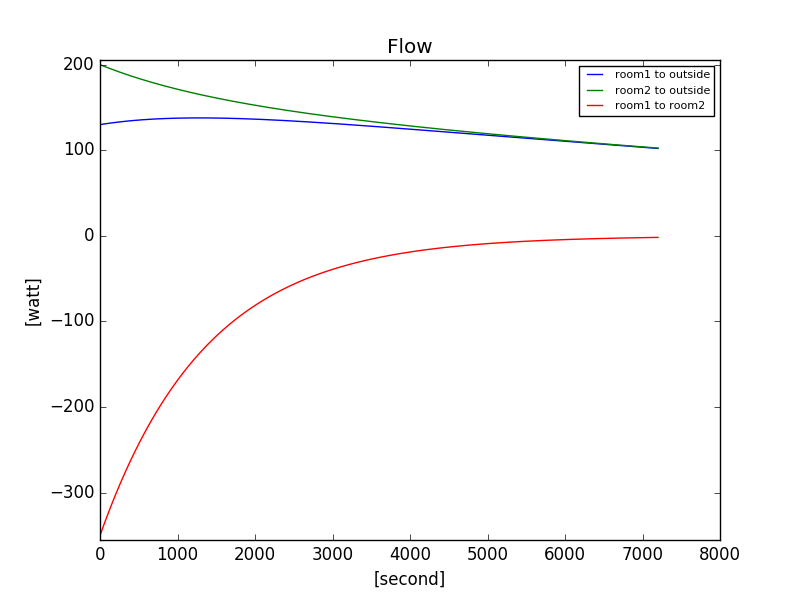
- On line 72, we use a second saver to save in a csv file the a recorder we already saved, here the 20th first lines:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | minute,outside,room2,room1
0.0,5.0,25.0,18.0
0.0166666666667,5.0,24.9963515755,18.0014593698
0.0333333333333,5.0,24.9927050871,18.0029169487
0.05,5.0,24.9890605334,18.004372738
0.0666666666667,5.0,24.9854179132,18.0058267391
0.0833333333333,5.0,24.9817772251,18.0072789533
0.1,5.0,24.9781384676,18.008729382
0.116666666667,5.0,24.9745016395,18.0101780265
0.133333333333,5.0,24.9708667394,18.0116248882
0.15,5.0,24.9672337658,18.0130699684
0.166666666667,5.0,24.9636027176,18.0145132685
0.183333333333,5.0,24.9599735932,18.0159547898
0.2,5.0,24.9563463914,18.0173945337
0.216666666667,5.0,24.9527211107,18.0188325015
0.233333333333,5.0,24.9490977499,18.0202686946
0.25,5.0,24.9454763076,18.0217031143
0.266666666667,5.0,24.9418567824,18.0231357619
0.283333333333,5.0,24.938239173,18.0245666388
0.3,5.0,24.934623478,18.0259957463
|
-
class
gridsim.iodata.output.AttributesGetter(self)¶ Bases:
objectThis is the based class for all data which have to be saved.
-
x_values(self)¶ This method returns x values of data stored.
Returns: a list of values Return type: list
-
x_unit(self)¶ This method returns x unit of data stored.
Returns: a string representing the unit. Return type: str
-
y_values(self)¶ This method returns y values of data stored. As more than one data can be sent, the values have to be sent with the following format:
[(label1, data1), (label2, data2), ...]with: * labelX: a string representing the dataX * dataX: a list of dataReturns: a dict of values Return type: dict
-
y_unit(self)¶ This method returns y unit of data stored.
Returns: a string representing the unit. Return type: str
-
-
class
gridsim.iodata.output.FigureSaver(self, values, title)¶ Bases:
objectA
FigureSavercan be used to record a class:.AttributesGetter and plot it in a file.Parameters: - values (AttributesGetter) – The values to display
- title (str) – The title of the plot.
-
x_label¶
-
y_label¶
-
figure¶ The matplotlib figure identifier. If the figure was not already rendered, it will do this by calling
render()automatically before actually returning the figure.
-
render(self, y_min=None, y_max=None)¶ Does the actual figure and returns the matplotlib figure identifier.
Note
you do not need to call this method explicitly as it will get called as soon as needed by other methods like
save()or the property getterfigureare called. This method offers some fine tuning parameters to control the look of the figure.Parameters: - y_min (float) – Minimal value on the y-axis.
- y_max (float) – Maximal value on the y-axis.
-
save(self, file_name)¶ Saves the figure in the given file (
file_name). The format is deduced from the file name extension. The output supported formats available depend on the backend being used. On Unix systems these formats are normally supported:Scalable Vector Graphics - *.svg, *.svgz (zip *.svg)
Graphics Interchange Format - *.gif
Portable Network Graphics - *.png
JPEG Image - *.jpg, *.jpeg
Postscript - *.ps
Encapsulated Postscript - *.eps
Tagged Image Format File - *.tif, *.tiff
Raw RGBA bitmap - *.raw, *.rgba
Portable Document Format - *.pdf
Parameters: file_name (str) – File name (path) where to save the figure. The file format is deduced from the file extension.
-
class
gridsim.iodata.output.CSVSaver(self, values, separator=', ')¶ Bases:
objectThis saver save data as a text file with the csv format with the given.
Parameters: - values (AttributesGetter) – The values to display
- separator (str) – the separator of two data in the same line
-
save(self, file_name)¶ Saves the data in the given file (
file_name). The format is a text file regardless the extension of the file. The data is store with the csv format and the header are the data returned bygridsim.iodata.output.AttributesGetter.x_unit()andgridsim.iodata.output.AttributesGetter.y_unit()Parameters: file_name (str) – File name (path) where to save the file.